Learn how to access the hidden Library folder in your Home folder on your Mac so you can tweak app settings and access app files.
Inside the home folder on your Mac is a Library folder that stores app-specific files and settings, personal settings, and some data. The files and settings in the Library folder should be left alone for the most part. But, you may want to tweak the settings for an app, which may require accessing the Library folder. Or, maybe an app backs up data to the Library folder and you want to copy that to an external drive.
As of Mac OS X Lion (10.7), the Library folder in your home folder is hidden by default. That doesn’t mean you can’t get to it. It’s hidden so you don’t accidentally delete settings and data, damaging apps in the process. So, if you decide you want to access the Library folder, be very careful.
Today we’re going to cover different ways of accessing the hidden Library folder in your home folder and how to make it permanently available in Finder.
What is the Path to the Library Folder?
Oct 03, 2018 Open Finder or just click on the desktop. Head to Go Go to Folder, or hit Cmd + Shift + G. Type: /Library in the Go to the folder box on the dialog box and click Go or press Enter. If you have one or more Finder windows open, the Library folder opens in the currently active window. Erase an application and it will leave preference files left over in your Library folders. Most of the time, these files will use very little space and won’t cause a problem. The preferences will still be available on your Mac, too — this is convenient if you’re uninstalling an app only to replace it with a newer version of the same app, or if you reinstall the app later down the line.
The Library in your home folder is written as ~/Library. The tilde (~) character is a shortcut for your home directory. For example, on my Mac, that would expand to /Users/lorikaufman/Library.
Access the Library Folder Using the Go to Folder Option
If you want to access the Library folder only occasionally, you can use the Go to Folder option in Finder.
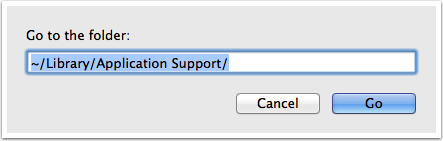
Open Finder or just click on the desktop. Head to Go > Go to Folder, or hit Cmd + Shift + G.
Type:~/Library in the Go to the folder box on the dialog box and click Go or press Enter.
If you have one or more Finder windows open, the Library folder opens in the currently active window. If no Finder windows are open, a new one opens to the Library folder.
Access the Library Folder Using the Terminal
If you prefer using the command line, you can access the Library folder using the Terminal.
Go to Utilities > Terminal in the Applications folder. To access the Library folder directly in the Terminal, type:cd ~/Library at the prompt to switch to the Library folder.
You can type:ls at the prompt to get a detailed folder listing. You can work with the files in the Library folder directly on the command line. Just be careful.
You can also use the Terminal to open the Library folder in a Finder window. Type:open ~/Library at the prompt and hit Enter.
Access the Hidden Library Menu Option in Finder
The Library folder is available on the Go menu in Finder, but it doesn’t show on the menu by default.
To temporarily show the Library option on the Go menu, open the menu and press the Option key. The Library folder shows up between Home and Computer on the Go menu. Keep the Option key pressed while you move your mouse down the menu and select Library.
If you’re using a Windows keyboard with your Mac, press the Alt key.
Show the Library Folder Permanently in Finder
If you access the Library folder often, you can permanently show the Library option on the Go menu and the Library folder in your Home folder.
Open Finder and head to your Home folder using the left pane or by pressing Cmd + Shift + H. Then, go to View > Show View Options, or hit Cmd + J.
A dialog box displays with options you can set for your Home folder. Check the Show Library Folder box at the bottom of the dialog box. The Library folder now shows up in your Home folder in Finder windows and the Library option becomes permanently available on the Go menu.
When you permanently show the Library folder in Finder, you can hit Cmd + Shift + L to open it in a Finder window, in addition to selecting the Library option on the Go menu.
Happy Tweaking, But Be Careful
The Library folder is hidden by default for a good reason. So, before tweaking settings and changing files in the Library folder, make sure you know what you’re doing.
All files and folders that you encounter when browsing the Finder in OS X should be displayed in regular font and icon color; however, there may be times when this is not the case, and one or more folders may appear grayed out and otherwise faded. When this happens, you will not be able to open the folder, and unlike other folders that may show a small entry triangle next to them in list view, these will not have options for viewing what is inside.
This display usually means the folder is not accessible at a low level, and this in turn is likely from either a fault in the filesystem entry for the file, or damage to your Mac’s hard drive formatting. This damage may happen from an interruption in a file or folder copying process, such as might happen from a power failure, crash, hard-reset, forced-cancel, or sudden disk unmount. This can also happen if you are using an unsupported storage setup, such as a software RAID array (especially those from third-parties), in which case you might see many (if not all) of your folders duplicated (see below).
Folder Named Knowledge On My Mac Applications Library System
Otherwise accessible folders may appear grayed and be inaccessible (click image for larger view).
Regardless of the reason, the result is you cannot open the folder, and other programs may not be able to open it either.
Overcoming the problem
This problem should be distinguished from the viewing of hidden folders in the Finder. OS X contains a number of hidden folders to keep your system looking clean, but there are hidden settings that can be activated to show these folders. When done, the folders will appear grayed; however, unlike this problem, they will be accessible. Nevertheless, for starters, open the Terminal utility (in Applications > Utilities) and run the following command to disable this hidden folder view (if enabled):
One potential cause for this issue is if the interruption caused the system to improperly set the folder’s creation or modification dates. Since the fix for this is relatively easy, this should be the first step you try for recovering the lost folder:
- Open the Terminal utility (in Applications > Utilities)
- Type the following command, followed by a single space (this space is important). The first eight digits here represent the date and time, in this case being January 1, 2015, with the trailing zeros being hours, minutes, and seconds, indicating midnight. This is a relevant date and time for a folder to be created:
- Copy and paste, or drag and drop, the grayed-out folder from the Finder to the Terminal window, so its full path is entered after the previously typed command (again with a space between the last number and the pasted file path). If you cannot select the file, then drag its parent folder to the Terminal window, followed by deleting the trailing space and then appending a slash followed by the folder name (i.e., “/foldername”) to the folder path.
- Press Enter to run the command, which will update the access and modification time stamps for the file.
Mac Library Folder Missing
Drive Repair Tools
If the above approach does not work, then your best bet to recover your drive is to reformat it and restore your Mac from a backup; however, if for some reason you need to preserve your drive (e.g., you do not have a backup), then alternative approaches include using drive utilities in an attempt to repair your drive. Apple’s Disk Utility can be used to run a general fix on your drive (when done in Recovery Mode); however, for directory corruption issues, Alsoft DiskWarrior and some other third-party tools may be useful. With these tools, you can attempt a directory rebuild, or filesystem repair routine, and see if these will fix any errors and make the folder and its contents available again.
Recovering data from the folder
Hopefully you have a backup of your files so you can safely format your drive if needed; however, if not then before formatting to clear the problem, you might be able to recover the data stored in the problematic folder by using a sequence of Terminal commands:
- In the Finder, create a folder named “Temp” on your Desktop
- Select the problematic grayed-out folder, and press Command-C to copy its path.
- Open the Terminal utility
- Type “mv -v” followed by a single space, and then press Command-V to paste the copied folder path.
- Press Delete once and then type “/* ” with a single space following the asterisk.
- Locate the new Temp folder on your Desktop, and then similarly select it and press Command-C to copy its path.
- Paste the path in the Terminal, so the full command will look similar to the following:
With this command assembled, pressing Enter should move the folder’s contents to the new Temp directory. You should see each file listed as it is moved, and when done the Terminal will drop you back to the command prompt. You can now back up the files, and then consider formatting your drive and restoring your files.
Managing Software RAID arrays
If this problem is happening for all folders on a software RAID array setup and resulting in all folders showing up in grayed-out duplicate, then the problem is very likely with your RAID configuration, and you will need to fix it either using the configuration utilities for your array, or by backing up your data, destroying the array, and rebuilding it. If the problem continues, then your RAID array might have a faulty drive, in which case you might look into replacing it, or optionally moving to another RAID setup that might be more compatible with your drives and your Mac.