Now, as for the files inside the various library folders: Most of them are organized by type (e.g. There's a Preferences folder, a Caches folder, an Application Support folder, etc) with files/subfolders per application (or system component, or whatever). A final reason to clear cache on Mac. Cache data works wonders for your Mac and system, but over time it can pile up and slow down your Mac’s performance, taking up the increasing amounts of space. Hopefully, our guide will be everything you needed and more to free up gigabytes of valuable space and reclaim it by cleaning cache. Apr 14, 2017 Since Mac OS 10.7 Lion, /Library directory, which saves files(including caches) for apps to run, is hidden in Mac system. So it needs a little work to access the.
| Click here to return to the 'Delete caches and save disk space' hint |
---
zs
For an Intel equivalent of the disk space usage, try Disk Inventory, also free.
Also, to skip the typing everytime & for a graphical interface, these options are available in both maintenance tools of Onyx and iTweax.
The heavier-duty Onyx actually doesn't indicate the amount used by the Cache, which the light-weight iTweax does.
I recently recovered 5 gigs of hard drive space using Tiger Cache Cleaner. My iBook also starts up and runs noticeably faster now.
$ du -k ~/Library/Caches/ | sort -n
Great for spotting where that space is going
(you may need to sudo it)
$ sudo -k ~/Library/Caches/ | sort -n > du_cache.txt
to get a text file
Doesn't work...
---
Father of Jeremy Logan
---
Father of Jeremy Logan
just use a . (ie. period) in place of pwd... and no quotes. FYI: in unix the . stands for the current directory and a .. stands for the parent directory.
It's easier than that!
du -k | sort -n
du defaults to the present directory
(Comparable to TreeSize on Win-Systems)
-- brf
---
--
Adam C.
I'm not sure if this hint has been posted before but if you get info on each application file there are installed language options. I went through all of my apps and deleted all of them except english. Most times this will halve the size of the app. Apple is notorious for installing 12 different languages for each app. I believe there is an apple script that does this automatically too.
Just be careful about deleting some application localizations. Some applications may have dependencies to those localizations. Some time ago, I remember a problem when someone tried to delete localizations, and they ended up having to reinstall that application.
Yep, certain apps can mysteriously misbehave after you've deleted their language localization files. And Apple software updates can reinstall ones you've deleted so it's not necessarily a one-time removal routine.
I don't see any reason to risk removing those files unless reclaiming disk space is a necessity and there are no safer alternatives.
I can recommend Monolingual (monolingual.sourceforge.net), a neat little software that does just that - removes language resources you don't want/need. I've been using it for a couple of years now without problems (making sure never to remove any of the English varieties (my system language).
Anders
Just for reference, I will reiterate what has already been said about the long-term importance (or lack there of) of files in the ~/Library/Caches directory.
Recently I discovered a bug in an application (the producer of said application was 'some kind of fruit company' who shall remain nameless), and the top level tech that I was working with confirmed that its no big deal to delete the contents of the ~/Library/Caches directory.
I'm not advocating that you empty the directory and then lock the folder so that it can never be populated, nor am I advocating that you empty the directory at all. I'm simply stating that you can empty the directory and its not a big deal.
If your Caches folder is out of control, then you should think about some sort of cleaning.
For comparison purposes, here are the current sizes for my (Mac OS X created) Caches folders:
/Library/Caches
24.7 MB
/System/Library/Caches
11.6 MB
/private/var/root/Library/Caches
16 KB
~/Library/Caches
80.2 MB
The oldest directory within the ~/Library/Caches directory was modified Apr 4 2006.
I'd be cautious deleting ~/Library/Caches/Metadata because it contains Spotlight proxy files used by iCal, Safari, and other apps. Something will eventually trigger those files to be regenerated but before that happens Spotlight searching may be temporarily crippled. I discovered that awhile ago with Safari bookmarks and eventually deleted and restored the Bookmarks.plist file to force proxy files to be rebuilt after other methods had failed to do it.
First, a true confession: Until very recently (i.e. today) I didn't know about the need to periodically delete the cache and as a result, mine was gigantic.
I deleted the cache by dragging it into the trash and then emptying the trash. Then I told the computer to restart. I understand it takes awhile to rebuild the cache, but I'm not sure what 'awhile' means. It's been almost 2 hours now and I'm wondering if that's normal for the (gulp) years worth of stuff that was stored in my cache. How many hours should I let this continue before taking some other action?
Thanks for your help.
You’ve probably heard and seen the term 'cache' used on your Mac but do you know what it is?
Cache files are basically temporary data stored on your hard drive and used to speed up processes. For instance, Safari will download images on a webpage into cache so that next time you visit the site you don’t have to download the images again.
How are cache files different from cookies?
Cookie files are tiny members of the big cache family. This form of cache is collected by your browser to remember previously visited websites. Cookies collect the details of your visit, its duration, actions on a page, etc. Advertisers also use these to follow you around the internet. However annoying they are, cookies are a part of internet reality that we cannot help but “Accept.”
There are many reasons to remove old cache from your MacBook and disk space issue is only one of them. So what are the other benefits ?
- Fixing issues with laggy web pages that load outdated content
- Removing personal data stored by websites and applications.
- You need to force-delete outdated cache from an app.
Are you ready to reclaim space on your Mac? Let’s go!
What are main cache types?
There are roughly three main types of caches you can clean on your Mac:
- System cache
- User cache (including app cache and DNS cache)
- Browser cache.
This article will go over cleaning up all three.
Now, when it comes to clearing cache on Mac, there are two ways you can do it. You can clean them up manually step-by-step, or you can clean them in second with a cleaning utility like CleanMyMac X. If you want to clear cache on your Mac right now, we suggest doing it the easy way:
- Launch CleanMyMac X (2019 version is preferable)
- Select System Junk
- Click 'Scan', and then “Clean”
That’s it, all cache files cleaned! CleanMyMac X works on all systems, including the latest macOS Catalina. You can download CleanMyMac X for free here and try.
However, if you’d like to clean them all manually, follow the steps below.
How to empty user cache on Mac?
Potential space reclaimed from junk - Up to 70%
As you can see, a single user cache folder on my computer takes up enormous 1.6 GB of space. And that’s just one folder out of hundreds. That means a good cleaning could free up gigabytes of free space and speed up your Mac in the process.
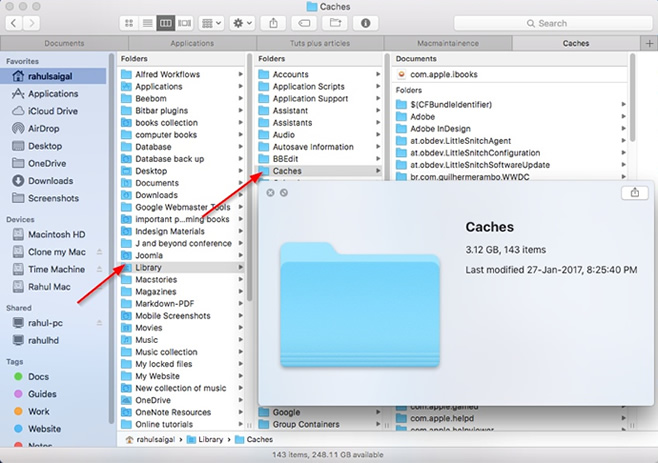
To clear your user cache, do the following:
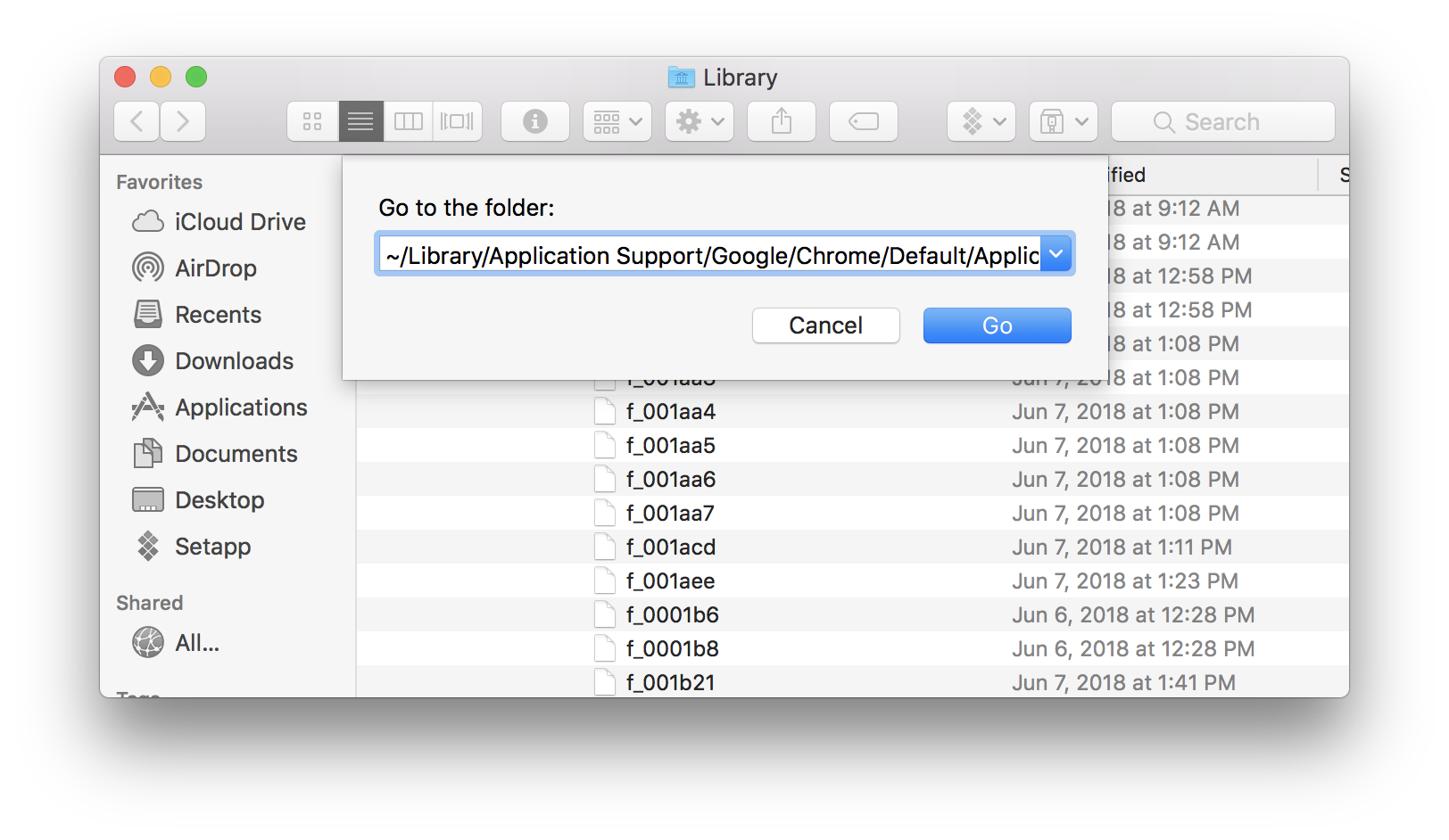
- Open a Finder window and select “Go to Folder” in the Go menu.
- Type in ~/Library/Caches and hit enter to proceed to this folder.
- Optional step: You can highlight and copy everything to a different folder just in case something goes wrong.
- Go into each of the folders and clean out everything.
Note: We recommend that you remove the insides of these folders, but not the folders themselves.
Now, repeat the same steps above, but substitute…
~/Library/Caches with… /Library/Caches
Make sure that once you have finished clearing out these caches for additional hard drive space, you empty out your Trash. To do this, Control-click on the Trash icon in the dock and select “Empty Trash.” Restart your Mac afterward so your Mac can begin to create new, fresh cache files.
To help you make sense of your Library folder here's a brief explanation what each sub folder stands for.
4 main types of cache within Library folder
Caches
Temporary data created by apps and websites. Your apps keep generating cache files for as long as they are active. Relying on such pre-loaded content reduces memory load and speeds up data exchange.
Preferences
Prererences folder is where you’ll find customized settings for your apps. Sometimes, there is a need to reset an app and delete its corrupted Preferences file. Preference files always end with .plist — so they are easy to spot and delete.
App support
App support folder contains large pieces of app data, like game saves. App support files may remain on your Mac long after you’ve deleted the app itself. That’s why “cleaners” for system junk were invented.
Containers
Containers folder is an exchange buffer that apps use to communicate with one another. This is often referred to as “sandboxing.” Containers folder is automatically emptied after you restart your Mac.
If you aren’t comfortable with the risk of deleting user cache manually, a specialist cleaning app CleanMyMac X can do it for you. It will only remove files you don’t need and will find up to 7x more temporary cache files to remove from all over your system.
How to delete system and app cache on Mac
Potential space reclaimed from junk - Up to 10% (manual methods) or 15% (using cleaner)
Next up we’re looking at your system cache files. These hidden cache files are mainly created by the apps that run on your Mac.
What is app cache? In short, it’s any media downloaded by the apps you use in order to work faster and not load it every time you open the app. Do you need it? It’s debatable, but app cache takes up disk space and can be cleaned.
You can delete app cache on Mac in the same way as user cache, by going to ~/Library/Caches and removing the insides of the folders with the app name.
Proceed with caution! Not all app cache can be safely cleared. Some app developers keep important user info on cache folders. Backing up a folder before you delete is always a good idea. If everything works fine then you can delete the backup later.
To be on the safe side, use CleanMyMac, it works with a Safety Database and knows how to clear app cache safely. As if that wasn’t enough it will also remove more junk than manual methods.
How cache is created? An example from Photos
Every time you do image manipulations, like rotating a picture, its additional copy is created on your drive. In this manner, just 4 rotations are enough for an image size to grow from 2.5 MB to 10 MB of disk space taken. If you edit photos and videos on a regular basis, you may notice that your editor application also keeps temporary data — like intermediate version of your files.
Library Folder Mac
How to clear browser cache on Mac
Potential space reclaimed from junk - Up to 15%
We all love to surf the web but every site we visit adds to the growing browser cache. Clearing your browser cache doesn’t just free up space, it will can also clear your browsing history to secure your privacy.
Browser cache temporarily stores website data such as images, scripts, and other stuff, in order to make your browsing faster when you revisit the same site. If you’re worried about your privacy or want to hide pages you’ve visited, you can clear your Internet cache (or browser history). Also, resetting your browser cache will potentially help to get rid of 404, 502, and other errors caused by corrupted cache.
Each browser has its own cache location, so the process of clearing is different in each case. For instance, Chrome cache location is in Settings, Safari stores its cache in Privacy, and Firefox cache location is History tab.
Here’s a quick introduction into how to delete browser cache on Mac.
How to clear cache in Chrome
Here’s how to clear browser cache in Chrome manually:
- Click the 3-dot icon in the top right corner of Google Chrome browser.
- Choose Settings.
- At the bottom of the menu, choose Advanced.
- Click “Clear browsing data.”
- Deselect all, but Cached images and files.
- Timewise, choose All time.
- Hit “Clear data” button.
How to clear cache in Firefox
Here’s how to delete cache in Firefox manually:
- Click the hamburger icon in the top right corner.
- Choose Privacy & Security on the left sidebar.
- Scroll to the section 'Cached web content' menu item.
- Now, click Clear Now to delete Firefox cache.
- Exit/quit all browser windows and re-open the browser.
In the same menu, checkmark Override automatic cache management and limit the cache size in MB. Go with the default amount of 350 MB, which is enough for most users' needs.
TIP:
If for some reason you cannot open a web page, try putting cache: in front of the URL address. This redirects you to the site’s cached copy.

For example: cache:macpaw.com
It works most of the time and can magically open even the otherwise blocked sites.
How to clear cache in Safari
Safari is a little trickier than the rest of the browsers. You could remove caches together with all the other website history through History — Clear History in menu bar.
But if you need more precision, here’s how to empty cache on Safari browser:
- In the top menu, choose Safari.
- Click Preferences.
- Choose the Advanced tab.
- Enable Show Develop menu in menu bar.
- Now go to Develop in menu bar.
- Choose Empty caches.
Make sure you close/quit the browser and restart it after clearing cache. Note, that all your auto logins and predicted websites in the address bar will be cleared.
Manual methods remove most of the browser junk but if you want to remove all of it, from all your browsers at once, there’s a safer and faster method to clear your internet cache on any browser.
How to clear cache files on Mac with a single click of a button
Instead of searching all over your Mac to find and remove cache files yourself, you can clear user caches on a Mac using CleanMyMac X. It makes removing cache files as easy as can be.
To get rid of cache files with CleanMyMac X:
- Download CleanMyMac X (free) and launch it.
- Select Smart Scan in the left menu.
- Hit Scan at the bottom of CleanMyMac X.
- Then click Clean.
And you're done! If you’d like to remove only cache files and nothing else, click on Review Details before clicking Clean. Deselect everything but System Cache Files and User Cache Files, then click Clean.
The easy way to clear all browsing data
Instead of clicking between browsers and being limited to what they let you clean, take full control of all your browser cleaning with this simple method:
- Open CleanMyMac and select the Privacy module
- Click on your browser of choice
- Make your selections from the list of all your cache and privacy tracks
- Click Remove to clean your browser
Cleaning your Mac has never been easier. Download CleanMyMac X and try for free to get yourself a faster, cleaner Mac — without worrying about cleaning the wrong thing.
And if you’re looking to clear just browser cookies, check out this easy one-minute explanation we’ve made for you.